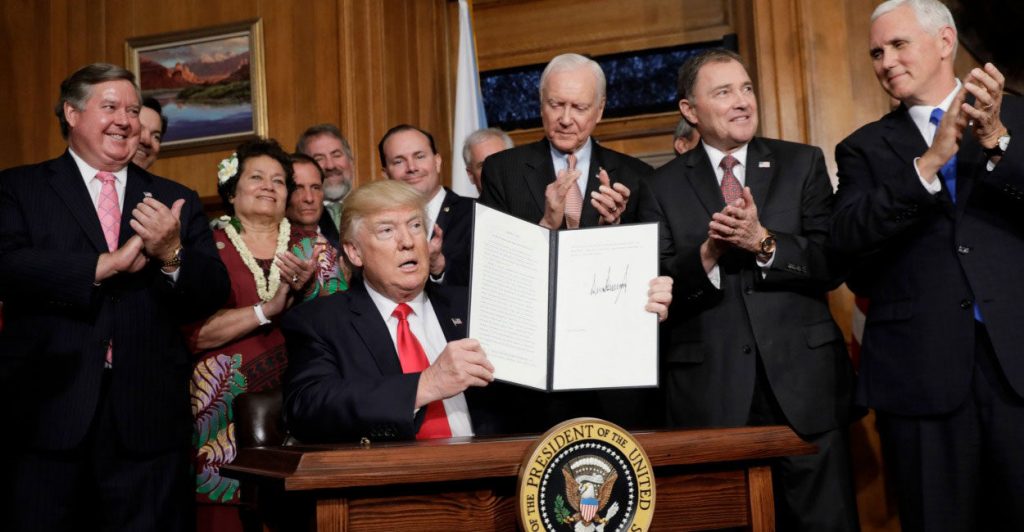

What is done by executive power can be undone by executive power.
Former President Barack Obama began to learn that lesson this Wednesday when President Donald Trump signed an executive order directing Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke to conduct a review of all Antiquities Act designations larger than 100,000 acres over the past 30 years.
Specifically, the executive order directs Zinke to consider “the requirements and original objectives of the Act, including the Act’s requirement that reservations of land not exceed ‘the smallest area compatible with the proper care and management of the objects to be protected’” and whether “designated lands are appropriately classified under the Act as ‘historic landmarks, historic and prehistoric structures, [or] other objects of historic or scientific interest.’”
>>>See our article of November 21, 2016, by the late Utah Speaker of the House, Becky Lockhart: Western Lands Must Be Returned to States
This wording strongly suggests that Obama’s lame duck decision to designate 1.35 million acres in San Juan County as a national monument will at least be significantly reduced and possibly entirely rescinded.
Some environmental activists may claim that Trump does not have the power to shrink or revoke Obama’s Antiquities Act designations, but these claims are ignorant of both history and the law.
For starters, as University of California Berkeley Law School professor John Yoo and Pacific Legal Foundation Executive Director John Gaziano detailed in a recent legal report, five presidents have significantly reduced four previous monument designations, and no one has ever questioned the legality of those reductions. [pullquote]in his discretion, to declare by public proclamation … national monuments …. the limits of which in all cases shall be confined to the smallest area compatible with proper care and management of the objects to be protected.[/pullquote]
Specifically, President Ike Eisenhower reduced the Great Sand Dunes National Monument by 25 percent, President Harry Truman reduced the Santa Rosa Island National Monument by 49 percent, Presidents William Howard Taft, Woodrow Wilson, and Calvin Coolidge collectively reduced the Mount Olympus monument by 49 percent, and Taft reduced the Navajo National Monument by 89 percent.
A current president’s power to alter a previous president’s flows from the text of the statute, which authorizes the president “in his discretion, to declare by public proclamation … national monuments …. the limits of which in all cases shall be confined to the smallest area compatible with proper care and management of the objects to be protected.”
As Yoo and Gaziano point out, “there is no temporal limit” on the requirement that a monument must be limited to “the smallest area compatible with proper care and management of the objects to be protected” so all presidents must use their ongoing discretion as to whether every monument is the proper size.
“What is done by executive power can be undone by executive power.”
Furthermore, what if a later president determines that an earlier president’s designation was so exceedingly beyond the “smallest area compatible with proper care” that the entire designation was illegal?
Yoo and Gaziano argue that the entire monument designation could be revoked.
Whatever Zinke does end up recommending to Trump—and a preliminary report is due in 45 days on Utah’s Bears Ears National Monument—further executive action will only be the beginning of solving San Juan County’s public lands issues.
Congress will then need to pick up the Public Lands Initiative legislation that was working through the House before Obama derailed the legislative process and pass a commonsense solution that includes real input from local residents.
Only through the legislation can local residents, including the Navajo, be given real power over their land use decisions.


 When Neil Gorsuch won long-overdue confirmation this month to serve on the United States Supreme Court, Republicans in turn won control of judiciary. This meant they led all three branches of the federal government – at least the three envisioned by our Founding Fathers – for the first time in a decade.
When Neil Gorsuch won long-overdue confirmation this month to serve on the United States Supreme Court, Republicans in turn won control of judiciary. This meant they led all three branches of the federal government – at least the three envisioned by our Founding Fathers – for the first time in a decade.
 The education problem has been growing in America for decades, as the costs of educating our children skyrocket and students are churned out of the public education system and universities with less and less actual education.
The education problem has been growing in America for decades, as the costs of educating our children skyrocket and students are churned out of the public education system and universities with less and less actual education.
 This will replace the current Student Loan program, which essentially supports a bloated, ineffective higher education system that is little more than a propaganda arm of the global leftist movement. It will also eliminate the current juggernaut of student debt, hanged around the neck of most graduat
This will replace the current Student Loan program, which essentially supports a bloated, ineffective higher education system that is little more than a propaganda arm of the global leftist movement. It will also eliminate the current juggernaut of student debt, hanged around the neck of most graduat A good place to start is President Donald Trump’s executive order, which calls for a review of national monument designations—a tool long used by presidents to unilaterally restrict land use. Also, see our article of November 21, 2016,
A good place to start is President Donald Trump’s executive order, which calls for a review of national monument designations—a tool long used by presidents to unilaterally restrict land use. Also, see our article of November 21, 2016, 
 A U.S. Navy destroyer had another close encounter with an Iranian Revolutionary Guard “fast attack craft” in the Persian Gulf Monday.
A U.S. Navy destroyer had another close encounter with an Iranian Revolutionary Guard “fast attack craft” in the Persian Gulf Monday.
 FBI Director James Comey distrusted former Attorney General Loretta Lynch and senior officials at the Justice Department, believing they might provide
FBI Director James Comey distrusted former Attorney General Loretta Lynch and senior officials at the Justice Department, believing they might provide  Trump Succeeds Where Obama Failed for Years
Trump Succeeds Where Obama Failed for Years
 Howard Dean Claims The First Amendment Doesn’t Protect Ann Coulter Expressing her Traditional Opinions
Howard Dean Claims The First Amendment Doesn’t Protect Ann Coulter Expressing her Traditional Opinions
 A civil war has begun.
A civil war has begun. The left was enormously successful in this regard. It was so successful that it lost all sense of proportion and decided to be open about its views and to launch a political power struggle after losing an election.
The left was enormously successful in this regard. It was so successful that it lost all sense of proportion and decided to be open about its views and to launch a political power struggle after losing an election.


 Aaron Hernandez, the former New England Patriots star who was convicted of murder in 2015, killed himself in his prison cell Wednesday morning, officials said.
Aaron Hernandez, the former New England Patriots star who was convicted of murder in 2015, killed himself in his prison cell Wednesday morning, officials said. Fresno shooting spree: 3 people killed, suspect who yelled ‘Allahu Akbar,’ says he ‘hates white people’ in custody
Fresno shooting spree: 3 people killed, suspect who yelled ‘Allahu Akbar,’ says he ‘hates white people’ in custody
 In a recent
In a recent 
 Video released by the Pentagon on Friday showed the “Mother of all Bombs” plummeting from the sky and exploding in eastern Afghanistan, as military officials said it flattened a cave-and-tunnel complex controlled by the Islamic State terror group.
Video released by the Pentagon on Friday showed the “Mother of all Bombs” plummeting from the sky and exploding in eastern Afghanistan, as military officials said it flattened a cave-and-tunnel complex controlled by the Islamic State terror group. GOP SURVIVES FIRST TEST
GOP SURVIVES FIRST TEST
 DEVELOPING: A California elementary school is currently on lockdown after 4 people reportedly were shot there Monday in what police suspect is a murder-suicide.
DEVELOPING: A California elementary school is currently on lockdown after 4 people reportedly were shot there Monday in what police suspect is a murder-suicide.
Let’s take a look at past predictions to determine just how much confidence we can have in today’s environmentalists’ predictions.
In 1970, when Earth Day was conceived, the late George Wald, a Nobel laureate biology professor at Harvard University, predicted, “Civilization will end within 15 or 30 years unless immediate action is taken against problems facing mankind.”
Also in 1970, Paul Ehrlich, a Stanford University biologist and best-selling author of “The Population Bomb,” declared that the world’s population would soon outstrip food supplies.
In an article for The Progressive, he predicted, “The death rate will increase until at least 100-200 million people per year will be starving to death during the next 10 years.”
He gave this warning in 1969 to Britain’s Institute of Biology: “If I were a gambler, I would take even money that England will not exist in the year 2000.”
On the first Earth Day, Ehrlich warned, “In 10 years, all important animal life in the sea will be extinct.”
Despite such predictions, Ehrlich has won no fewer than 16 awards, including the 1990 Crafoord Prize, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences’ highest award.
In International Wildlife (July 1975), Nigel Calder warned, “The threat of a new ice age must now stand alongside nuclear war as a likely source of wholesale death and misery for mankind.”
In Science News (1975), C.C. Wallen of the World Meteorological Organization is reported as saying, “The cooling since 1940 has been large enough and consistent enough that it will not soon be reversed.”
In 2000, climate researcher David Viner told The Independent, a British newspaper, that within “a few years,” snowfall would become “a very rare and exciting event” in Britain. “Children just aren’t going to know what snow is,” he said. “Snowfalls are now just a thing of the past.”
In the following years, the U.K. saw some of its largest snowfalls and lowest temperatures since records started being kept in 1914.
In 1970, ecologist Kenneth Watt told a Swarthmore College audience:
Also in 1970, Sen. Gaylord Nelson, D-Wis., wrote in Look magazine: “Dr. S. Dillon Ripley, secretary of the Smithsonian (Institution), believes that in 25 years, somewhere between 75 and 80 percent of all the species of living animals will be extinct.”
Scientist Harrison Brown published a chart in Scientific American that year estimating that mankind would run out of copper shortly after 2000. Lead, zinc, tin, gold, and silver were to disappear before 1990.
Erroneous predictions didn’t start with Earth Day.
In 1939, the U.S. Department of the Interior said American oil supplies would last for only another 13 years. In 1949, the secretary of the interior said the end of U.S. oil supplies was in sight.
Having learned nothing from its earlier erroneous claims, in 1974 the U.S. Geological Survey said the U.S. had only a 10-year supply of natural gas.
The fact of the matter, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, is that as of 2014, we had 2.47 quadrillion cubic feet of natural gas, which should last about a century.
Hoodwinking Americans is part of the environmentalist agenda. Environmental activist Stephen Schneider told Discover magazine in 1989:
In 1988, then-Sen. Timothy Wirth, D-Colo., said: “We’ve got to … try to ride the global warming issue. Even if the theory of global warming is wrong … we will be doing the right thing anyway in terms of economic policy and environmental policy.”
Americans have paid a steep price for buying into environmental deception and lies.
By Walter E. Williams